AI Governance in Insurance: Trust, Transparency, Transformation
AI Governance: The Foundation for Responsible Innovation in Insurance
The insurance industry stands on the edge of an AI revolution. Artificial intelligence is already reshaping underwriting, claims, fraud detection, customer experience, and back-office operations. Yet the real question is no longer “What can AI do?”… it’s “How can we use it responsibly?”
AI Governance provides the blueprint for doing exactly that. It defines the policies, oversight mechanisms, and human controls that ensure AI systems are transparent, fair, explainable, and aligned with business goals and societal values. For insurers, it’s the difference between using AI effectively and using it ethically.
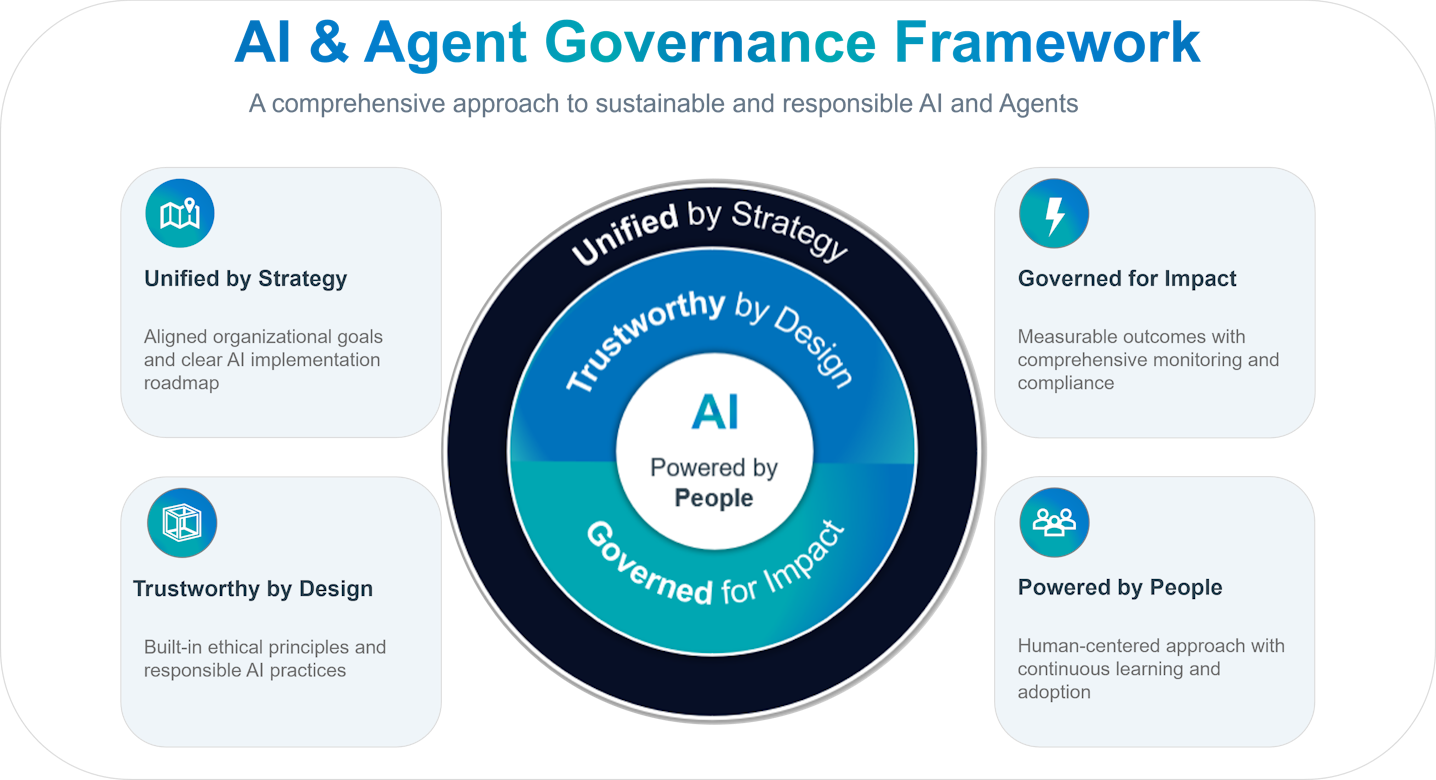
At NTT DATA, we believe the most successful insurers will be those who approach AI transformation through four interlocking principles:
Unified by Strategy. Trustworthy by Design. Governed for Impact. Powered by People.
1. Unified by Strategy: Embedding Governance into the Business Core
Many insurers have dabbled with automation pilots or analytics tools, but AI must be part of a unified enterprise strategy to truly deliver value. Governance ensures every AI initiative aligns with corporate objectives, risk appetite, and long-term vision.
When governance is woven into strategic planning:
Shadow AI deployments are prevented.
Compliance risk is reduced.
AI investments are evaluated through measurable business outcomes.
Senior management and board-level committees should oversee AI policy formation, vendor selection, and risk review. This top-down accountability creates a governance culture that is proactive to evolving regulations from the NAIC, EIOPA, and the EU AI Act.
2. Trustworthy by Design: Building Confidence into Every Decision
Insurance is a business built on trust. Every claim filed and every premium calculated carries a promise of fairness and transparency. That promise must now extend to AI.
To be trustworthy by design, insurers should implement:
Bias detection and mitigation throughout model development.
Explainability tools such as model cards, lineage mapping, and audit logs.
Privacy and security controls protecting sensitive policyholder data.
Regulators are already setting expectations. For example, New York’s DFS Regulation 187 requires AI systems to demonstrate they do not produce discriminatory outcomes. Similarly, NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework 1.0 outlines principles for trustworthy AI: reliability, safety, explainability, and fairness.
Explainable AI doesn’t just protect consumers; it strengthens confidence among employees and regulators, paving the way for sustainable adoption.
3. Governed for Impact: From Compliance to Continuous Improvement
AI governance is not about red tape. It’s about results. As AI systems become more complex, insurers need robust frameworks to ensure that technology innovation aligns with ethical, legal, and business standards.
An effective AI governance model includes:
A complete inventory of all AI and agent systems.
Clear accountability between business owners and technical stewards.
Continuous monitoring for bias, drift, and unintended outcomes.
Governance integration across procurement, deployment, and retirement workflows.
Regulatory bodies such as the NAIC and the EU AI Act advocate for risk-tiered oversight, meaning high-risk AI (like pricing and underwriting) requires greater scrutiny and documentation.
Insurers can operationalize this by starting with low-risk automation, such as document classification, policy servicing, or claims intake, before expanding to higher-risk domains.
4. Powered by People: Human Oversight Drives Responsible AI
Even the smartest algorithms depend on human wisdom. The insurance industry will always be powered by people. Their judgment, empathy, and ability to see beyond the data.
Strong AI governance establishes human-in-the-loop, human-on-the-loop, and human-in-command mechanisms that allow oversight and intervention when needed. This layered structure ensures AI acts as an assistant, not an authority.
Equally important is workforce enablement. As intelligent automation handles repetitive work, employees can focus on higher-value activities like customer consultation and risk analysis. NTT DATA’s research shows that well-governed automation not only improves productivity but also boosts morale and innovation.
Training programs in AI ethics, compliance, and literacy empower staff to identify risks early and champion responsible innovation from within.
5. Agentic AI in Action: Governance for the Next Generation of Automation
AI’s evolution toward Agentic AI introduces new opportunities and responsibilities.
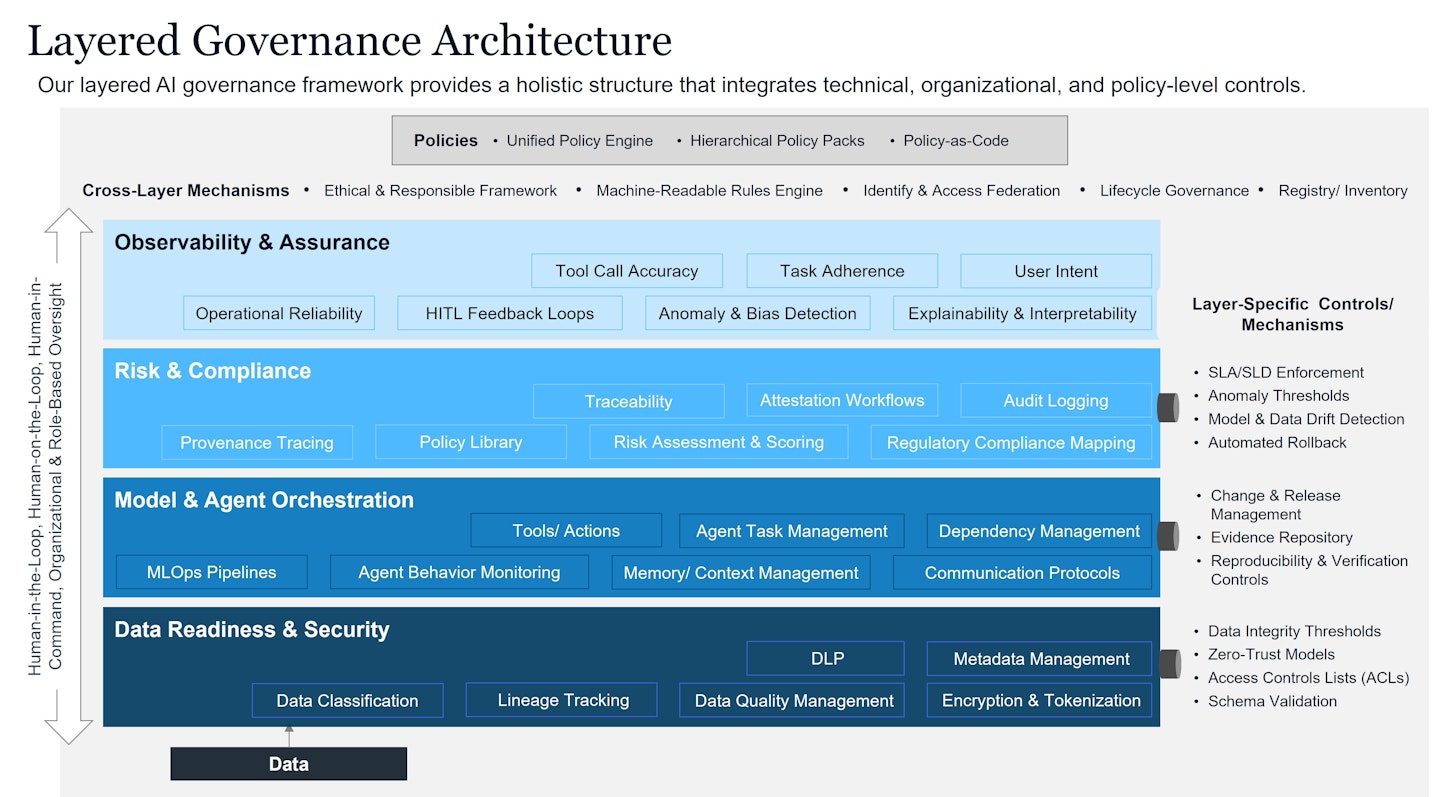
NTT DATA’s Governance Architecture uses modular layering that allow for independent updates and continuous improvement on each part. It relies on mechanisms such as hierarchical policies and deterministic machines-readable rules and interactive components to ensure governance is scalable, adaptive and audit-ready across all AI systems.
The Bottom Line: Responsible AI Is Good Insurance
The insurance industry has always been about managing risk and protecting trust. These values perfectly align with AI governance. As technology reshapes underwriting, claims, and customer service, governance ensures those systems reflect the fairness, accountability, and reliability that define the industry itself.
By committing to the four principles, unified by strategy, trustworthy by design, governed for impact, and powered by people, insurers can build the resilient, ethical, and future-ready organizations policyholders expect.
In the end, the future of insurance won’t be defined by algorithms alone,
it will be defined by how responsibly we govern them.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest insights about Global solutions for leading insurers on your email




