Unleashing the Power of Super Apps
What is a Super App?
A Super App is an application with several services inside one single platform. According to Gartner:
A Super App, or super-app is an application that provides end users (customers, partners, or employees) with a set of core features plus access to independently created mini-apps. The Super App is built as a platform to deliver a mini-app ecosystem that users can choose from to activate for consistent and personalized app experiences.
These multifaceted platforms offer an extensive array of services under a single digital roof, introducing unprecedented convenience and redefining the user experience. While these super apps have captured the hearts of users across Asia, particularly in countries like China and Southeast Asia, their journey to establish dominance in the European market is a complex endeavor, especially when we talk about integrating insurance services into the equation.
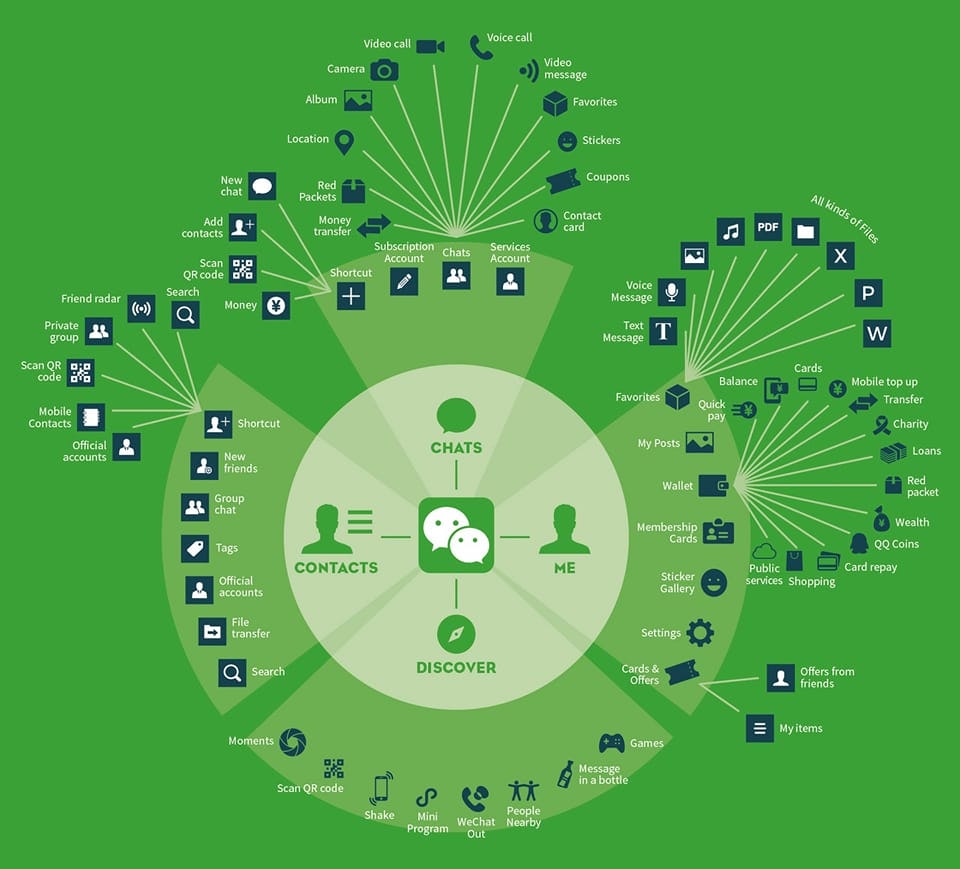
Introduction of Chinese successful Super Apps
In China, the Super Apps are a common practice among tech players. Metuan, WeChat, Alibaba, and Ping An count with multifaceted apps with several services and products being offered on the same platform for the end customer. These players were not born with multiple services, instead, they grew strong in a specific vertical and expanded to complement their offerings and ultimately enhance their value proposition.
Take WeChat as an example. WeChat was born as a simple messaging and photo-sharing app in 2011, since then the brand included hundreds of new features like WeChat pay, shopping, and mobility services. The last feature of WeChat is the mini-Programs, in which third parties can create a mini-app inside the WeChat platform. Hence, the company went from a messaging app to a comprehensive platform with Social, Content, Games, Shopping, and Services.
WeChat is not an isolated example. Metuan, a Chinese shopping platform has also humble beginnings. The company was founded in 2010 as an Asian Groupon that offers discount coupons, but currently, customers can Review restaurants, rent a bike, order food, buy movie tickets, and more. Nowadays, Metuan is the biggest player in the Chinese food delivery market. The history and evolution of Supper Apps in China raise an important question: Can supper apps traction in other markets like Europe or the USA?
Answering this question is relatively straightforward: Most likely not, at least not following the approach used in China, but it can be achieved with some adjustments.
The challenge to replicate Super Apps
Successful Asian Super Apps have peculiarities that are hardly replicated in other markets. We identified the most relevant challenges that can be divided into 3 parts: Data, Culture, and Market Fit. The first point is of course the way companies, customers, and the government approach data storage, exchange, and analysis. Secondly, cultural differences are key to the traction of several businesses on the same platform. The last point is related to intrinsic economic and societal structure, in which Super Apps fit greatly.
Data
The concept of Closed Loop is essential to understanding how data is leveraged by companies to match customers’ expectations. The concept of a closed loop revolves around the idea of retaining consumers within a single application ecosystem, catering to their entire lifecycle of needs. The importance of establishing a closed loop lies in its ability to facilitate Super Apps in achieving the following objectives:
Customer Retention: Super Apps do not need to start from scratch when acquiring new customers. Instead, they can seamlessly transition customer demands from one service to another, from one usage scenario to another, thereby maintaining strong user engagement.
Enhanced User Experience: To create a sustainable closed loop, the process typically involves steps such as obtaining recommendations, converting users, facilitating purchases, collecting feedback, encouraging repurchases, and promoting user referrals.
Data-Driven Personalization: Leveraging data analytics plays a crucial role in this process. By analyzing user data, Super Apps can unearth potential demands and offer personalized services based on data intelligence. The more data they accumulate, the more accurate their algorithms become in predicting user preferences.
Diverse Portfolio: Super Apps can effectively combine a diverse portfolio of services and products within their ecosystem. This includes offering free services, low-margin but high-frequency services, high-margin but low-frequency services, and other relevant offerings.
However, customer data might be an issue if the company is trustworthy and provides value enough to convince users to share their data and be satisfied with what it brings in exchange. Trust in organizations is on average higher in Asian and Latin countries as pointed out by the Edelman Trust Barometer.

Moreover, Asian Super Apps delivers a seamless experience that is the consequence of accurate online profiling due to advantageous regulation and customer trust in the organizations. Regulatory issues have a clear impact on the development of Super apps, to illustrate differences in Government support for Super Apps we do not have to go too far. While Meta, Google, and Apple leaders are constantly in Congress hearing about data issues, WeChat and Alipay users can access public services and the government has their own account on these platforms.
Culture
In the Asian market, particularly in countries like China, the success of Super Apps is significantly influenced by the unique cultural dynamics at play. China's historical continuity and a large population sharing a common language, culture, and values have fostered a deep sense of unity and homogeneity. Unlike regions with diverse immigrant cultures, in the Confucian tradition, immigrant cultures are integrated seamlessly within the society, further strengthening this cohesion. This homogeneity extends to consumption habits, where people often rely on recommendations from their social circles to inform their purchasing decisions.
Asian culture's emphasis on practical functionality over aesthetics is also mirrored in the design ethos of their apps, a notable departure from the visually stunning but sometimes less functional European counterparts. Asian apps prioritize usability, aligning perfectly with the streamlined design philosophy of Super Apps. This practical approach resonates with users, making their daily interactions more efficient.
Furthermore, the close-knit cultural fabric and shared languages in many Asian countries foster strong communities, which, in turn, drive the network effects that Super Apps rely upon. Recommendations and interactions from friends and family hold significant weight in decision-making processes.
The holistic engagement offered by Super Apps, blending social interactions and commerce, is particularly potent in cultures where personal relationships have a substantial impact on purchasing decisions. In essence, the success of Super Apps in the Asian market is intricately tied to the region's cultural values, its emphasis on functionality, and the significance of personal connections in daily life and commerce.
Market Fit
This point is strongly connected to the cultural structure. The Asian market exhibits a strong demand for Super Apps, driven by several factors that make this model particularly appealing to the region. For instance, in Southeast Asia, a significant portion of the population remains unbanked or underbanked, lacking access to traditional financial services.
Super Apps play a pivotal role in addressing this gap by providing a wide range of financial services, from digital payments and money transfers to micro-loans and insurance. This empowers individuals who were previously excluded from the formal banking system to participate in the digital economy. This financial inclusion aspect has made Super Apps immensely popular among the unbanked and underbanked populations in Southeast Asia.
Moreover, Asia is home to a predominantly mobile-first population. With a rapidly growing middle class and increasing smartphone penetration, mobile devices have become the primary gateway to the Internet and digital services. Super Apps are specifically tailored for mobile use, offering a one-stop solution for various needs, including communication, shopping, transportation, and financial services. The convenience of having all these services accessible through a single mobile app aligns perfectly with the preferences of the mobile-centric Asian population.
Super Apps application for Insurance
The development of Super Apps is opening opportunities for the insurance industry to expand its revenue potential and become closer to end customers. The idea of embedding insurance products in third parties’ platforms impacts the way insurance reaches customers and how customers perceive insurance.
Let us take a look at Nubank's case, the Latam Fintech Giant. Nubank started in Brazil as a digital bank with a simple application and a credit card. In fact, the company is responsible for giving the first bank service and products for about 50% of its 32 Million clients in 2020. By the end of that year, Nubank launched life insurance protection in partnership with Chubb and probably gave the first contact with life insurance to millions of Brazilians. The traction or margin of this life insurance product is not relevant when we compare the intangible benefits of giving access or the first contact with such an iconic insurance product that probably would not reach as many people. Obviously, this is one particular case, but it can help us to expand our imagination on how many doors can be opened with embedded insurance to close the gap between insurers and end customers.
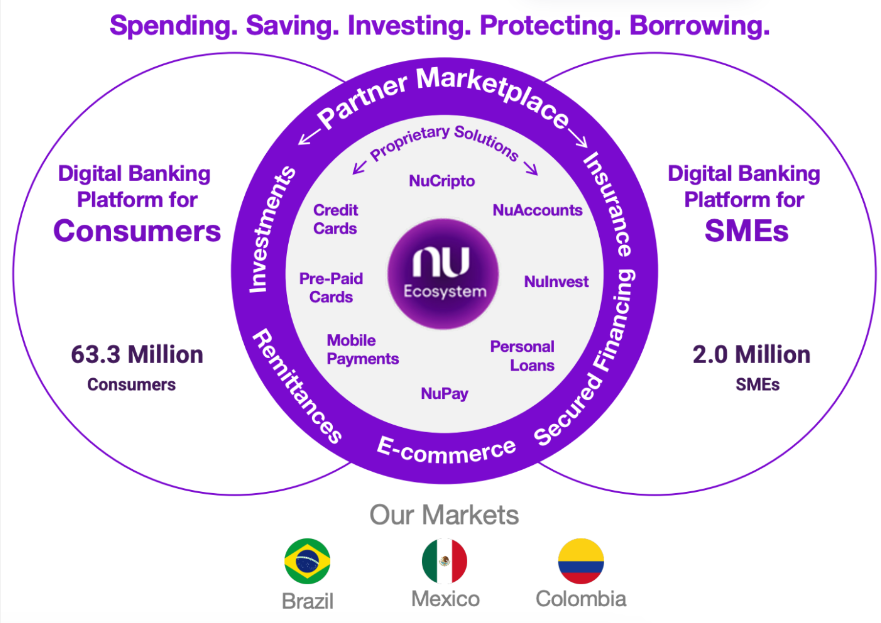
Going back to China. Both WeChat and Metuan started with dear products for end customers, which are a messaging app and a food delivery service, respectively. Insurance products are not quite the same they are not as desired, making it much harder to scale and acquire a mass customer base. One can argue that Ping An did exactly that going from a small insurance company to a tech conglomerate and a Super App with 600 M users. However, Ping An is an exception to the rule, most Insurers have issuers to create successful end customers applications for one single line of business.
In fact, the trend of D2C insurtech with appealing apps appears to have reached its peak a few years ago, most of them struggling to expand and become profitable. Currently, as pointed out in the Insurtech Report 2023, most of the focus in the Insurance sector is on the B2B side: Climate Change, Smart Distribution, Employee Benefits, and Underwriting. Although, it is very unlikely that in the near future Super Insurance Apps become successful, Super Apps are on the rise in both emerging markets and advanced markets.
In Europe and the USA Super Apps products and services gravitate strongly towards their core business, making Super Apps in the USA and Europe focused on one vertical or indirectly replicating it by creating other brands inside an ecosystem. For instance, Revolut is a fintech with a Super App that offers insurance, lending, investments, credit cards, and more financial products. And the indirect super app that Google created for end customers that can access through different applications under the same parent company.

Therefore, the concept of Super Apps has taken root in the digital landscape, with its development differing between Asia and Europe/USA. While the blueprint of Asian Super Apps may not seamlessly translate to Western markets, the trend of Super Apps, if we broaden the scope a little bit, is becoming global. Insurance Super Apps, however, face unique challenges due to low customer desire and scalability issues. Nevertheless, the insurance industry can leverage the Super App trend by forging strategic partnerships, as exemplified by Nubank's collaboration with Chubb, to bridge the gap between insurers and end customers.
Despite the difficulties in introducing insurance Super Apps, the wider Super App trend continues to gain momentum globally. In Europe and the USA, Super Apps often revolve around core businesses and verticals, maintaining a focus on specific services. While Super Insurance Apps may face hurdles in the immediate future, the concept of super apps is flourishing in both emerging and advanced markets, reshaping the way Insurance connects with customers and offers its services.
The main common points in the Super Apps development route
Initiating from the most rapidly expanding market as the entry point: Businesses often launch in markets where growth is substantial and the potential for adoption is high. This strategic choice allows for quick traction and establishes a strong foundation for expansion into other markets.
Focused efforts on mass customer acquisition: Aiming to acquire a significant number of customers in a relatively short period, companies deploy targeted marketing, user-friendly onboarding, and appealing offers to attract a large user base.
Venturing into new verticals and expanding services: To diversify revenue streams and cater to varied customer needs, businesses expand into different industries or offer complementary services that align with their core offerings.
Placing customer needs at the core of operations: By prioritizing customer feedback and preferences, businesses can design products, services, and experiences that genuinely resonate with their audience, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Staying attuned to market trends: Adapting to market trends, especially during exceptional circumstances like a pandemic, ensures businesses remain relevant and continue to meet changing consumer behaviors and needs.
Building strong customer loyalty based on data: Offer exceptional customer experiences, personalized offerings, and consistent communication to increase customer retention, based on data analytics. This helps build a sustainable closed loop from the perspective of user experience: receiving a recommendation-conversion-purchase-feedback-repurchase-giving recommendation to others.
Broadening partnerships and considering acquisitions: Collaborating with partners and considering acquisitions can provide access to new markets, technologies, and expertise, accelerating growth and expanding the business's reach.
Striving for profitability: While growth is important, achieving profitability is a critical milestone for long-term sustainability. Businesses focus on optimizing operations, managing costs, and efficiently monetizing their offerings.
Directing the business to where the consumers are: Recognizing that consumers' preferences and behaviors shape market dynamics, businesses align their strategies to cater to these preferences, ensuring that their products and services are readily available and accessible to their target audience.
Header photo by Bagus Hernawan on Unsplash
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest insights about Global solutions for leading insurers on your email





